Story
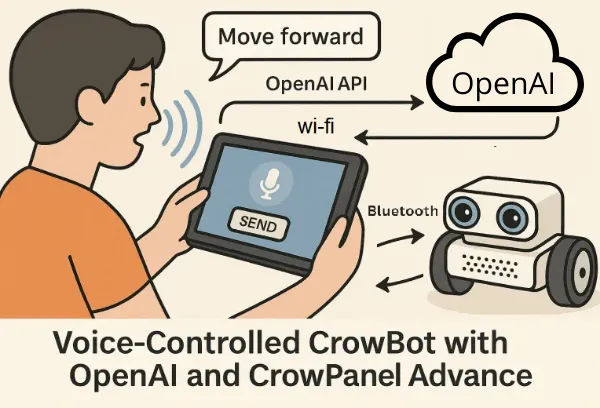
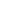
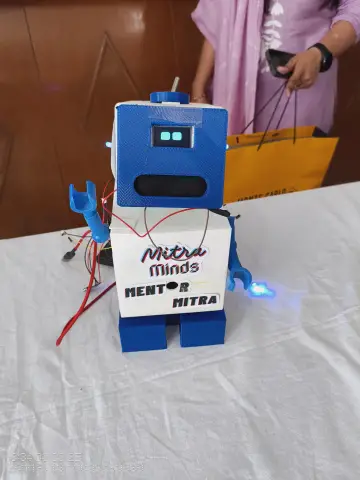
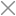
This project demonstrates how to build a compact, intelligent voice-controlled robot system using the CrowPanel Advance and the OpenAI Realtime API. The CrowPanel records the user's voice, sends it to OpenAI for transcription and interpretation, and receives a structured command. This command is interpreted on the panel and then transmitted to the robot (CrowBot) over Bluetooth.
Thanks to GPT-based natural language understanding, the robot can respond not only to simple instructions like “Go forward”, but also to indirect phrases like “It’s kind of dark in here” — and respond by turning on headlights.
While this setup works out-of-the-box with CrowBot, it can be easily adapted to control other DIY robotic platforms, Bluetooth-enabled smart toys, or even home automation systems.
🔗 Project repository: Grovety/OpenAI_Robot_Control
📽️ Demo video: Watch on YouTube
✨ Features
- - Hands-free voice control using CrowPanel Advance's built-in microphone
- - Natural language understanding powered by OpenAI (Realtime API)
- - Function calling via structured JSON for safe, extensible command execution
- - Bluetooth-based command transmission to CrowBot
- - Simple GUI for Wi-Fi setup and API key entry
- - Open-source and extensible: adapt it for your own robots or systems
⚙️ How It Works
-
The user holds the CrowPanel Advance, running a custom control application.
-
They speak a command — e.g., “Go forward and turn right”, or “It’s kind of dark in here”.
-
The voice is streamed to OpenAI Realtime API, where it is transcribed (via
gpt-4o-mini-transcribe) and processed. -
OpenAI returns a structured JSON with function names and parameters.
-
The CrowPanel interprets the response and transmits commands via Bluetooth to the CrowBot.
-
The robot executes the actions (e.g., moving, turning, lights on/off).
-
Unsupported or unclear requests are safely handled using a built-in
reject_requestfunction.
Thanks to the OpenAI integration, even complex or indirect voice commands are parsed into actionable steps, making robot control more intuitive and fun.
🔧 Required Hardware
- - CrowPanel Advance
- - CrowPanel Addon (with Bluetooth module)
- - CrowBot or any robot accepting Bluetooth UART commands
- - OpenAI API Key
🖥️ Firmware
CrowPanel firmware and voice control logic:
👉 Grovety/OpenAI_Robot_Control
Custom CrowBot firmware:
🛠️ Tutorial – Quick Start Guide
There are two installation options:
-
- A quick setup using prebuilt images
-
- A full build-from-source option for developers and makers
🔹 Option 1: Flash prebuilt firmware
-
Download
flash_tool.exefrom the repository with binaries folder
-
Connect CrowPanel via USB and run the flasher.

-
After flashing, connect to Wi-Fi

-
And input your OpenAI API key.

-
Power on CrowBot.
-
Start speaking — try commands like:
-
“Forward”
-
“Turn left and switch on the lights”
-

🔹 Option 2: Build from source
-
Clone the Grovety/OpenAI_Robot_Control repo
-
Use ESP-IDF v5.4+ to build and flash the CrowPanel firmware
-
Customize GUI, Bluetooth logic, or the command parser as needed
-
Flash CrowBot with compatible firmware using Arduino or PlatformIO
📦 About Command Processing
Instead of using a long text prompt, this project uses OpenAI’s function calling feature to safely map user speech to valid robot actions.
A JSON file defines all available functions:
👉 function_list_robot.json
Each function has a name (e.g. go_forward), a description, and optional parameters.
When the user says something like:
“Go forward and turn on the lights”
CrowPanel sends:
-
- the recognized text
-
- the JSON function list
-
- and the instruction
function_call: auto
OpenAI returns structured output like:
CrowPanel parses the result and sends corresponding Bluetooth commands to CrowBot.
✅ Why this approach is great:
-
- Only approved functions can be called — no surprises
-
- Adding new commands is easy — just update the JSON
-
- Supports safe fallbacks like
reject_requestfor unclear input -
- Scalable and secure — follows OpenAI's recommended architecture for embedded AI
🧪 Ideas for Expansion
Want to take it further? Here are some directions:
-
- Add a voice response system using a speaker and OpenAI’s voice synthesis
-
- Integrate a dialog system with contextual memory
-
- Use the same setup to control smart home devices via Bluetooth relays
-
- Combine it with gesture recognition or visual feedback
-
- Extend the command set via JSON — just update
function_list_robot.json -
- Switch from one-shot transcription to real-time voice ↔️ voice interaction using OpenAI's streaming API