Story
Project Overview: Real‑Time GPS Tracker with NodeMCU (No SIM Required)
Platform:
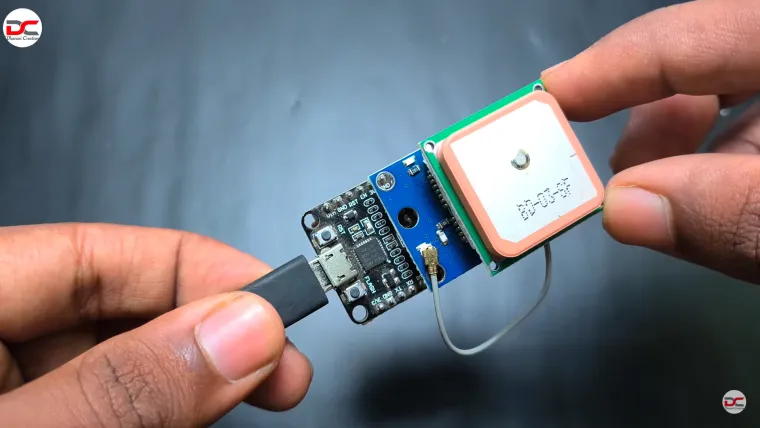
This is a real-time GPS tracking project built around the NodeMCU ESP8266 module and a Neo‑6M GPS module, powered by Wi-Fi rather than cellular networks .
Key Features:
-
Simple, cost-effective GPS tracking without SIM card or GSM network
-
Real-time transmission of GPS data (latitude, longitude, accuracy) over Wi‑Fi to a web or map interface (typically Google Maps)
-
The project is attributed to Dharani Creations, recently published (~last week)
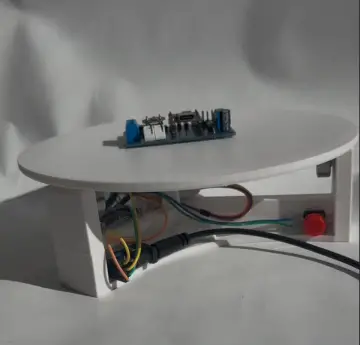
Hardware Components
-
NodeMCU ESP8266 board – microcontroller with built-in Wi‑Fi
-
Neo‑6M GPS module – provides NMEA GPS data via serial
-
Micro‑USB cable – for power and programming
-
Optionally a display (LCD/OLED) or serial interface for basic debugging (per other read‑alike tutorials)
Circuit Wiring
-
GPS TX → NodeMCU RX
-
GPS RX → NodeMCU TX
-
GPS power: 3.3 V (or VCC to VIN depending on board)
-
NodeMCU powered over USB from PC or power bank
-
(Optional) Add a display to show coordinates locally in real time
Firmware & Code Structure
-
Arduino IDE is used to write/upload code
-
Core logic:
-
Connect to predefined Wi‑Fi SSID/password
-
Read NMEA sentences from the Neo‑6M GPS to parse latitude/longitude
-
Send data periodically (e.g. every few seconds) to a server or live map interface over HTTP
-
Display or log coordinates via serial monitor or display
-
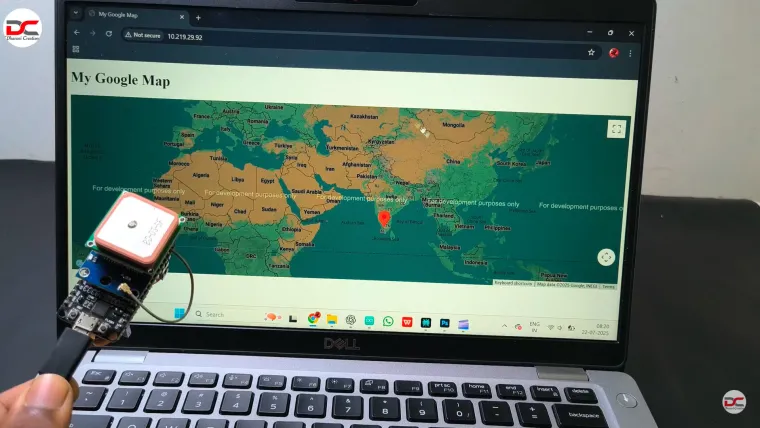
The video implies Google Maps integration for live tracking
-
Many tutorials (notably older ones like from JustDoElectronics or CircuitDigest) also include optional display feedback or local webserver hosting features .
Software Workflow (General Steps)
| Step | Operation |
|---|---|
| 1 | Import Wi‑Fi + GPS + JSON libraries (e.g., SoftwareSerial, TinyGPS++, ESP8266WiFi) |
| 2 | Initialize serial ports for GPS and debug output |
| 3 | Connect to Wi‑Fi at startup |
| 4 | In loop(): read GPS data, parse coordinates |
| 5 | If fix is valid, send JSON containing coordinates and accuracy to a web endpoint or Google Maps link |
| 6 | Repeat at set intervals (e.g. every 5 seconds) |
| 7 | Optionally buffer data if offline and sync when reconnected |
The code may also include minimal error handling to retry Wi‑Fi or GPS fix acquisition.
Extended Capabilities & Enhancements
Though not explicitly shown in the video, similar projects support:
-
Local display output (e.g. using 16×2 LCD or OLED) to show live coordinates
-
Offline data buffer: Store location data if Wi‑Fi is down, then upload once it comes back
-
Web interface / dashboard powered by simple server or Google Maps API for visualization
-
Adjustable update frequency and power-saving modes for long-term deployment
-
Status messages via serial like “Connected to Wi‑Fi”, “GPS fix acquired”, or error states
Summary
In short, the project is:
-
Built with NodeMCU ESP8266 and Neo‑6M GPS module
-
Sends your GPS coordinates over Wi‑Fi in real-time (no SIM card needed)
-
Integrates with mapping (e.g. Google Maps) to visualize live location
-
Flexible and low-cost—great for learning embedded IoT and GPS-based tracking
Suggestions if You Want to Recreate This
-
Gather hardware: NodeMCU + Neo‑6M module
-
Use Arduino IDE + required libraries
-
Implement logic to parse GPS NMEA output
-
Establish Wi‑Fi connectivity and HTTP POST/update logic
-
Create a map link or simple server to visualize location
-
Optional: add display or offline buffering
-
Test, tweak interval settings and accuracy thresholds