Story
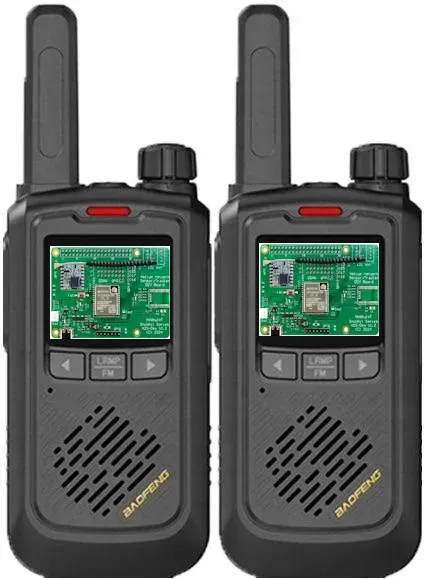
Using a LoRa module to build a walkie-talkie is an innovative project, but it’s quite different from traditional analog or digital voice walkie-talkies. LoRa (Long Range) is a low-power, long-range wireless communication technology designed for low data rate applications, like sensor data in IoT—not for continuous audio streaming. However, it can still be used for walkie-talkie-style communication with some trade-offs.
This LoRa walkie-talkie works by digitizing and compressing voice, sending it over LoRa in small data packets, and playing it on the receiver. It’s not real-time or full-duplex, but provides very long range, low power, and basic walkie-talkie functionality for voice messages.
1. Hardware Components
-
H2S – Dev board
-
Microphone (electret or MEMS) for audio input
-
Speaker or earphone for audio output
-
Audio codec (e.g., VS1053 or custom ADC/DAC) for compressing/decompressing audio
-
Push-to-Talk (PTT) button
-
Power supply (battery)
2. High-Level Working Process
a. Capture Audio
-
The microphone captures analog audio signals when the user presses the PTT button.
-
Audio is digitized using an ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) on the microcontroller or an external codec.
b. Compress & Packetize Audio
-
Raw audio is compressed (e.g., using ADPCM or other lightweight codecs) because LoRa has limited bandwidth (~300bps to 37.5kbps depending on settings).
-
The digitized audio is broken into small packets suitable for LoRa transmission.
c. Transmit Audio Over LoRa
-
The packets are sent sequentially over the LoRa radio.
-
Due to LoRa’s long range but low data rate, this is typically half-duplex and delayed (latency from buffering and packet transmission).
d. Receive and Reconstruct Audio
-
The receiving device listens for incoming packets.
-
It reassembles and decompresses the audio.
-
Finally, it outputs the audio through a DAC and speaker.
3. Key Considerations & Challenges
|
Aspect |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Latency |
LoRa is not real-time; expect a delay of ~100ms to several seconds depending on bitrate and compression. |
|
Audio Quality |
Low bitrate audio (e.g., 8 kHz, 4-bit ADPCM) results in lower quality, but intelligible voice. |
|
Duplexing |
Only half-duplex possible (talk OR listen, not both at once), similar to traditional walkie-talkies. |
|
Power Consumption |
LoRa is very low-power for data transmission, but audio processing (especially codecs) can consume more. |
|
Range |
Can reach 1-15+ km depending on environment, antenna, and power settings. Far exceeds typical walkie-talkies. |