Story
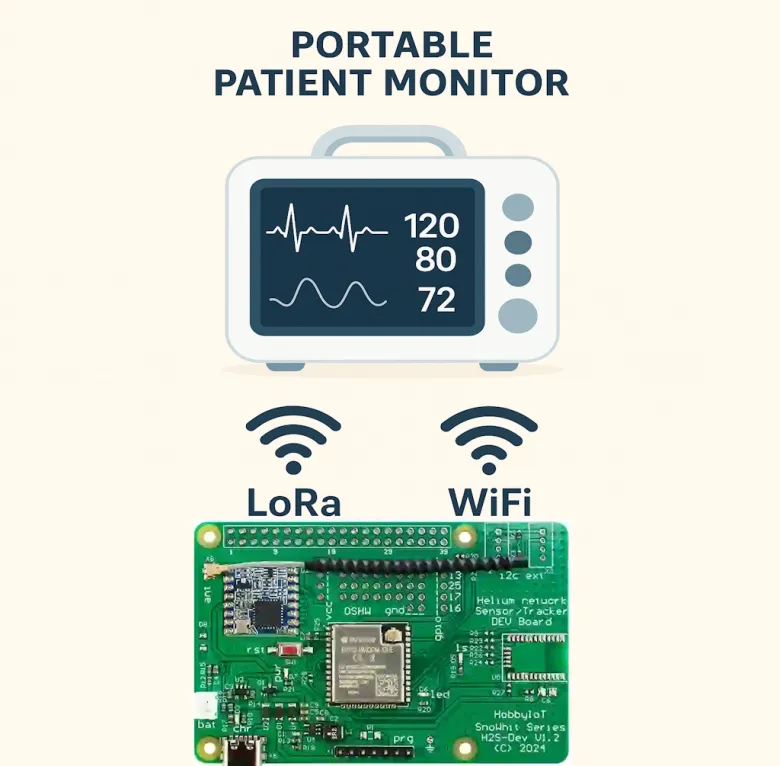
A LoRa and WiFi-based patient monitoring system is an excellent way to combine the long-range communication capabilities of LoRa and the high-bandwidth connectivity of WiFi to create a hybrid system that can monitor patient vitals in real-time and relay that data to healthcare providers or cloud servers.
LoRa is used for long-range, low-power communication when the device is far from WiFi, while WiFi provides high-speed data transfer when available. The system enables real-time monitoring, data collection, and alerts for healthcare providers or caregivers.
The LoRa and WiFi-based patient monitor allows remote, long-range monitoring of patient health data.
Applications
The proposed system can be used in the following applications
1. Home Patient Monitoring
The device uses LoRa when the patient is out of WiFi range (e.g., rural areas), and WiFi is used when the patient is in a connected home. Data is uploaded to the cloud and is accessible by the doctor or caregiver for remote monitoring.
2. Ambulance Monitoring
A patient in an ambulance can have their vitals continuously monitored. If LoRa is used, it can send patient data to the hospital or nearest medical facility for preparation before arrival.
3. Long-Term Care or Remote Areas
Elderly or chronically ill patients in remote areas can use LoRa to send their vitals to a nearby gateway or health center. In this scenario, WiFi can also be used when the patient is in a local facility with WiFi access.
List of elements used in the device
The device will consist of:
- H2S - Dev board containing an efficient ESP32 microcontroller with separate LoRa Module for long-range, low-power communication and WiFi module for high-bandwidth, short-range communication.
- Sensors to monitor vital signs like:
* Heart Rate (e.g., pulse oximeter sensor)
* Temperature (e.g., TMP36 or MLX90614 infrared thermometer)
* Blood Pressure (e.g., BMP180 sensor or dedicated cuff system)
* ECG signals (e.g., by AD8232 IC)
* Respiratory Rate
- Battery for portable, long-lasting power
- OLED or LCD Display to show real-time vitals to the user or patient.
- Push Button / Alert Button for the patient to request help or send an emergency signal.
- Cloud/Server/Local Database for data storage and real-time monitoring.
Description of operation
The system continuously measures the patient's vital signs using sensors (e.g., heart rate, temperature, blood pressure). The microcontroller processes this raw sensor data, and possibly filters out noise or applies basic algorithms (e.g., average heart rate, temperature trend).
When the device is out of range of WiFi or in a remote area (e.g., rural or emergency scenarios), the LoRa module can send sensor data in small packets to a nearby gateway, like a local monitor or LoRa base station. This could be useful for remote areas or for ambulance monitoring.
LoRa is used because of its long-range and low power consumption, making it suitable for sending critical data over a distance (up to 15 km in open spaces or more depending on terrain).
When the device is within range of a WiFi network (e.g., the patient's home network, hospital WiFi), the device can use WiFi to send the collected data to a cloud server or a local monitoring station. WiFi is better for real-time, high-bandwidth communication because it can handle more data and has lower latency than LoRa.
The microcontroller can send the patient’s sensor data (heart rate, temperature, etc.) to a cloud platform (e.g., ThingSpeak, AWS IoT, Google Firebase). The data can be processed and analyzed to track trends or send alerts to healthcare providers. Healthcare providers can access this data via a web portal or mobile app to monitor the patient's health in real-time.
If any critical vitals are detected (e.g., low heart rate, high fever, abnormal blood pressure), the system can trigger an alert (push notification or email) to the healthcare provider.
If the patient presses an emergency button, an alert message can be sent immediately over WiFi or LoRa to a caregiver or medical team.
LoRa is very power-efficient for transmitting small amounts of data, which is important for patient devices that need to last for extended periods without recharging.
Tasks of the monitoring system:
|
Task |
Action |
Communication Mode |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1. Monitor Vitals |
Sensors collect data (HR, BP, Temp, etc.) |
Local (on-device) |
Measure patient's health stats |
|
2. Initial Data Processing |
Microcontroller processes and filters data |
Local |
Prepare data for transmission |
|
3. Transmission (WiFi or LoRa) |
Send data to cloud or local monitor |
LoRa (long-range) or WiFi (local) |
Reliable data transfer |
|
4. Real-time Monitoring |
Healthcare provider receives data |
Cloud (e.g., ThingSpeak, Firebase) |
Track patient's vitals remotely |
|
5. Emergency Alert |
Patient presses emergency button or vitals cross thresholds |
LoRa or WiFi |
Send critical alerts to caregivers |