Story
Twin Cylinder Paddle Steamer Engine – A Mechanical Symphony in Motion
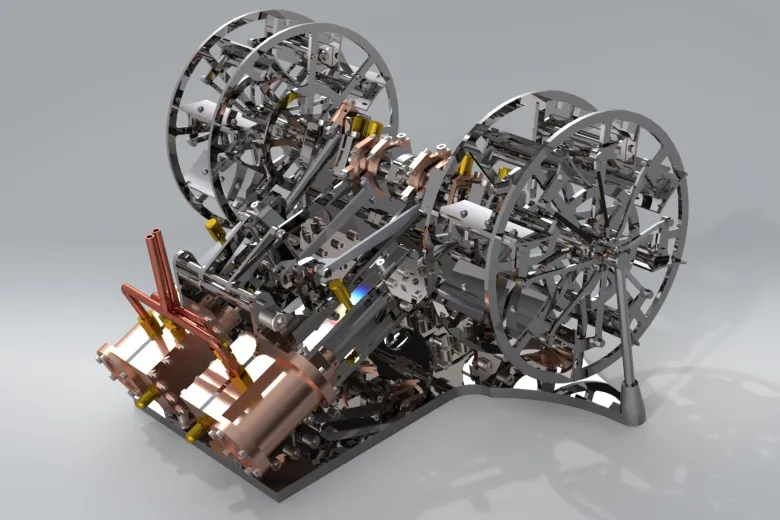
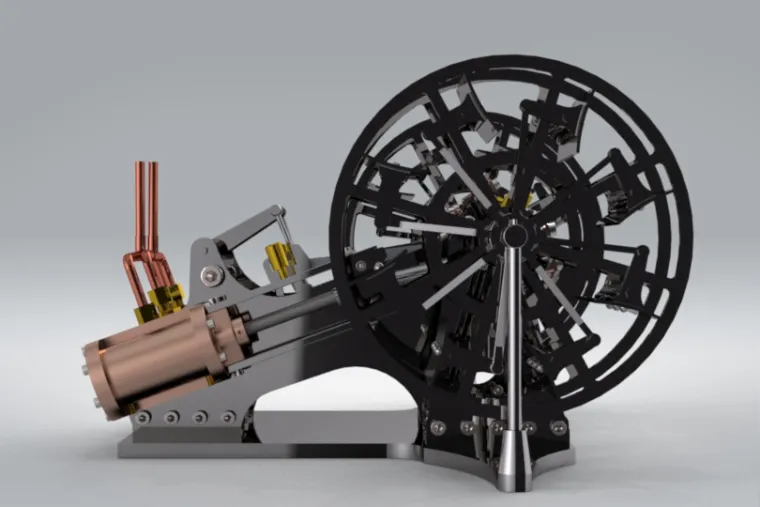
The Twin Cylinder Paddle Steamer Engine is a meticulously designed mechanical assembly inspired by the golden age of steam-powered transportation. This model captures the essence of 19th-century marine engineering, reimagined with precision CAD modeling, realistic mechanical linkages, and refined detailing to showcase both functionality and aesthetic depth.
At its core, the system operates on the principle of reciprocating steam engine mechanics, driving two large paddle wheels on either side of the frame. Each cylinder delivers power alternately, ensuring smooth, balanced propulsion — a defining characteristic of twin-cylinder configurations. The rhythmic motion of pistons, connecting rods, and crankshafts demonstrates how early engineers achieved efficient propulsion even with limited technology.
Design Overview
This paddle steamer engine has been modeled entirely from scratch in SOLIDWORKS, emphasizing accuracy, motion feasibility, and component interaction. Every linkage, bearing, and fastener has been designed to represent a functional mechanism rather than a static model. The assembly consists of hundreds of precisely constrained parts, highlighting a deep understanding of mechanical motion and realistic constraints.
The system features two main cylinders positioned symmetrically, each connected to its respective crankshaft through connecting rods. These crankshafts are synchronized by a central gear train to maintain uniform rotation of both paddle wheels. The motion from the pistons is thus transmitted efficiently to the outer paddle wheels, mimicking the thrust generation process that once powered classic steamboats across rivers and oceans.
Key Components and Mechanisms
-
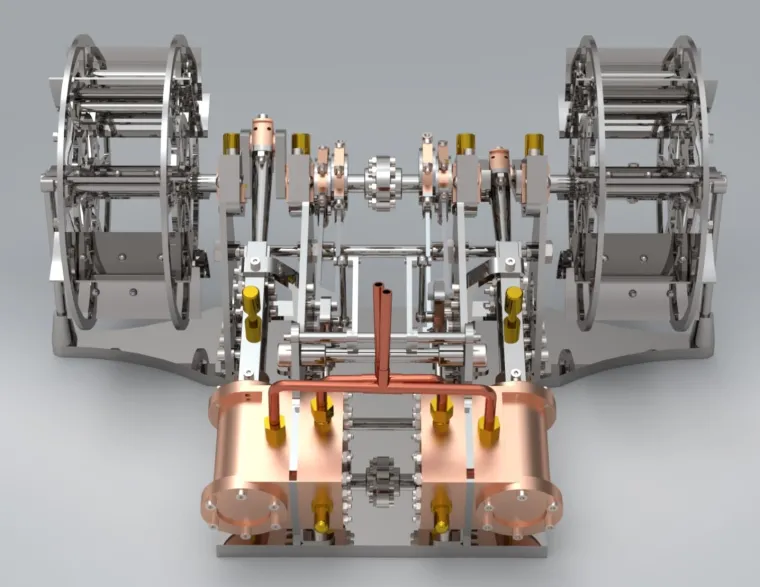
Twin Cylinders and Pistons:
The copper-toned twin cylinders form the heart of the engine. They house pistons that reciprocate under pressure, converting linear motion into rotational output. The piston rods are carefully aligned with the crank assembly to minimize friction and ensure smooth oscillation. -
Crankshaft and Flywheel System:
Each piston drives a crankshaft that translates reciprocating energy into rotary motion. The dual-wheel design uses a precise phase offset, providing continuous torque delivery and eliminating dead points during operation. -
Paddle Wheel Assemblies:
The two large paddle wheels, made of interlinked radial frames, replicate the propulsion units found in early marine vessels. Their design ensures balanced weight distribution and smooth fluid interaction when rotating through water. -
Valve Gear and Linkage Arrangement:
The valve system governs steam intake and exhaust timing, coordinated through an intricate linkage mechanism. This synchronization between valve motion and piston stroke ensures optimal power generation per cycle. -
Base Frame and Support Structure:
The entire mechanism is mounted on a rigid base frame that provides stability and alignment precision. The truss-like structure ensures minimal vibration transfer and serves as a robust platform for all dynamic components. -
Transmission Elements:
Chains, gears, and couplings are integrated to transmit power uniformly between both sides of the mechanism. The mechanical symmetry not only enhances efficiency but also provides a captivating visual rhythm when animated.
Material Representation and Aesthetic Balance
The choice of material finishes — polished steel, brushed copper, and brass accents — isn’t merely aesthetic. Each tone highlights a functional distinction: steel for structure and movement, copper for thermal elements, and brass for connectors and fittings. This contrast adds a sense of depth and realism, echoing the material palette of traditional steam machinery.
The reflections and render quality in the design emphasize the mechanical harmony of the assembly. Each nut, bolt, and pin has been carefully placed, making the model both visually impressive and mechanically coherent.
Purpose and Inspiration
The design serves as both a learning model and a tribute to classic steam power. It demonstrates how reciprocating engines translate raw energy into elegant mechanical motion — a concept that remains the foundation of modern mechanical design. This project represents not just technical skill, but also a deep passion for reviving the artistry and engineering ingenuity of a bygone era.
For me, this model isn’t just a CAD assembly — it’s an expression of mechanical creativity, discipline, and endless curiosity. Every joint and linkage is a reminder that true design is born from understanding both form and function.
Conclusion
The Twin Cylinder Paddle Steamer Engine is a blend of history, precision, and passion — a perfect example of how mechanical design continues to inspire even in the age of digital modeling. Designed entirely in SOLIDWORKS, it reflects not just technical proficiency, but an unwavering love for the art of engineering.
???? Explore the model on GrabCAD: https://grabcad.com/library/twin-cylinder-paddle-steamer-1