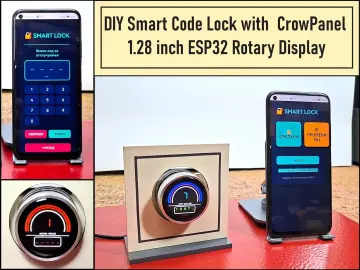
Story
Robotic manipulators with multiple degrees of freedom are widely used in industrial automation, research laboratories, and education. However, commercial robotic arms are often expensive and difficult to customize. Recent advances in additive manufacturing have enabled the development of low-cost robotic systems that can be fabricated locally and adapted to specific requirements.
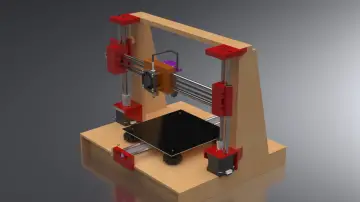
This work introduces a fully 3D-printable 6-DOF robotic arm with a gripper, designed to balance mechanical simplicity, structural rigidity, and ease of assembly. The project targets students, researchers, and makers who require a customizable robotic platform without the cost and complexity of industrial solutions.
The robotic arm consists of six rotational joints providing six degrees of freedom:
-
Base rotation
-
Shoulder pitch
-
Elbow pitch
-
Wrist pitch
-
Wrist roll
-
End-effector (gripper actuation)
Each joint is actuated using standard hobby servo motors, while structural components are designed as hollow beams to reduce weight while maintaining sufficient stiffness. The end effector is a parallel gripper suitable for basic manipulation tasks.
The arm links are implemented as hollow profiles to optimize the strength-to-weight ratio. Rotational joints are designed to accommodate servo shafts and bearings, ensuring repeatable motion and simplified assembly. The modular structure allows individual components to be reprinted or replaced without affecting the entire system.
The gripper is a parallel two-finger mechanism driven by a single servo motor. Its geometry is optimized for FDM printing and can be scaled or reshaped depending on the application. The gripper is suitable for handling small objects and educational manipulation tasks.
All components are designed for fabrication using Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). The parts can be printed on standard desktop 3D printers without specialized hardware.
Recommended printing parameters include:
-
Layer height: 0.2 mm
-
Infill density: 30–40%
-
Perimeters: 3–4
-
Material: PLA for prototyping, PETG for improved durability
Most parts can be printed without support structures, reducing material usage and post-processing time.
The robotic arm is assembled using standard M3 screws and nuts. Servo motors are mounted directly into the printed housings. The modular nature of the design simplifies maintenance and upgrades.
The proposed robotic arm is well suited for:
-
Robotics education and training
-
Rapid prototyping of manipulation systems
-
Research in kinematics and control algorithms
-
Integration with microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino) and robotics frameworks (e.g., ROS)
Due to its parametric design, the system can be extended with additional sensors, gear reductions, or alternative end effectors.
This project demonstrates that a functional 6-DOF robotic arm can be designed, fabricated, and assembled using low-cost tools and open-source software. The use of parametric modeling and additive manufacturing enables a high degree of customization while maintaining accessibility. The presented design provides a solid foundation for further development in educational and experimental robotics.