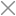
Story
???? Overview
This project demonstrates how to control an LED's blink rate in real time using two analog slide potentiometers and an ESP32.
A toggle switch is used to select which slider (A or B) is currently active, and a 16x2 LCD displays the active slider, its blink rate, and the inactive slider’s rate.
It’s a clean, practical project for learning analog input handling, non-blocking timing (millis), and LCD interfacing with ESP32.
⚙️ Features
- Dual analog slide potentiometers (
POT_A,POT_B) - Toggle switch for selecting the active slider
- Real-time LCD display of blink rates
- Non-blocking LED blinking using
millis() - Fully functional on breadboard (no external libraries beyond LiquidCrystal)
???? Working Principle
- Each potentiometer outputs an analog voltage (0–3.3 V) read via ESP32 ADC pins.
- The values are mapped to a time delay range (50 ms – 500 ms).
- The toggle switch decides which slider controls the LED’s blink rate.
- The LCD shows the current active slider (marked with
*) and the corresponding blink rate. - The LED blinks using non-blocking logic, ensuring smooth updates and display refreshes.
???? Components Required
| Component | Quantity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ESP32 Dev Board | 1 | Main microcontroller |
| 16x2 LCD (JHD162A) | 1 | Parallel interface LCD display |
| Slide Potentiometer (10 kΩ) | 1 | Analog input sliders |
| SPDT Toggle/Slide Switch | 1 | For slider selection |
| Jumper Wires | — | For connections |
| Breadboard | 1 | Circuit assembly |
???? Pin Connections
| Component | Pin | ESP32 GPIO |
|---|---|---|
| LCD RS | — | 12 |
| LCD E | — | 13 |
| LCD D4 | — | 14 |
| LCD D5 | — | 27 |
| LCD D6 | — | 26 |
| LCD D7 | — | 25 |
| POT A | Output | 34 |
| POT B | Output | 35 |
| Switch | Output | 33 |
| LED | + | 2 |
| LED | – | GND |
| LCD VCC | — | 5 V |
| LCD GND | — | GND |
???? Core Concepts Used
- Analog to Digital Conversion (ADC)
map()function for value scaling- Non-blocking delay using
millis() - LCD interfacing (parallel mode)
- State control with a toggle switch
???? Applications
- Demonstrating analog control and feedback systems
- DIY learning project for beginners in embedded systems
- Adaptive LED indicators
- Foundation for motor-speed or brightness controllers